How to create JButton in Java
In our previous post, we learned how to create a JFrame in Java. In this article, we will learn how we can create a JButton in java and add it to our JFrame.
The JButton is the class that is used to create a button in a JavaSE application. Use JButton to send actions to your application whenever a user interacts with the button by either clicking, hovering, etc.
Based on the official JavaDocs, a JButton is the actual implementation of a “push” button. It can be configured, and to some degree controlled, by Actions. Using an Action with a button has many benefits beyond directly configuring a button.
Creating a Jbutton in Java Example
package com.javapointers.javase;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
/**
*
* @author javapointers
*/
public class JButtonTest implements ActionListener {
JFrame frame;
JButton button;
public JButtonTest() {
frame = new JFrame();
frame.setTitle("My JFrame");
frame.setSize(500, 400);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
button = new JButton("Click Me!");
button.addActionListener(this);
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
frame.add(button);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("You have clicked the button");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
JButtonTest test = new JButtonTest();
}
}
When we run the program, it will show our JFrame with its JButton:
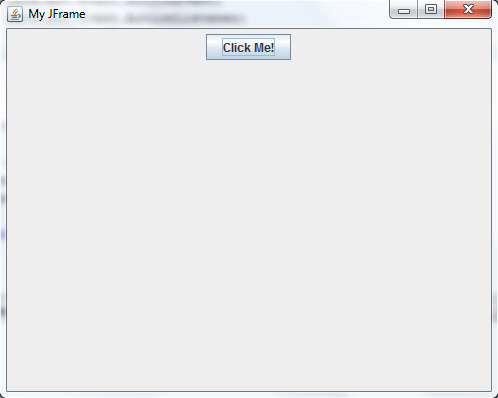
and when the user clicks on the button, the string “You have clicked the button” will be displayed in the console.
Explanation:
- import javax.swing.JButton – import the JButton class to be able to use it.
- button = new JButton(“Click Me!”) – Create a new instance of JButton with label Click Me!
- button.addActionListener(this) – Adds action when the user clicks the button.
- frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout()) – Define how java will layout your components. You will learn more about layout manager later on this tutorial.
- frame.add(button) – add the button to the frame.
- public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) – the method that will be called when the user clicks the button.
Now that we have learned how to create a JButton in Java, our next topic will be on how we can create a JPanel in Java that can hold other components including the JButton that we just discussed.