How to install Redis
Redis is a nosql mem-cached database. Since it is cached in memory, the read and write are fast. Although Redis is cached in memory, it can persist in your file system. Unlike mem-cached database, when you turn off your system, redis still holds the data that you have written. In this post, we will install redis in a debian based linux system.
1.To Install Redis, download Redis Sources
The first thing is to download the stable version of redis using:
wget http://download.redis.io/redis-stable.tar.gz
After finishing downloading redis, extract the files by using the command:
tar xvzf redis-stable.tar.gz
2.Compile Redis
After extracting the files, navigate to the folder by
cd redis-stable
Then we will compile the source code using
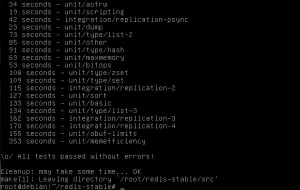
make
This will produce different output. You should see something similar to this when compiling.
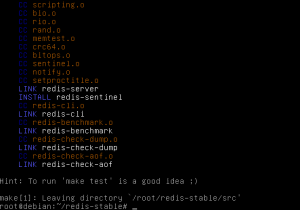
Lets try if our build works correctly by typing
make test
if for some reason you have been prompted something like you need tcl 8.5 or newer, you can resolve this by downloading tcl 8.5
sudo apt-get install tcl8.5
then try again to make test. Your test should pass by now.
3. Copy Files
After test succeeded, go to the src folder by
cd src
Then copy the redis-server and redis-cli to your local variables by:
sudo cp redis-server /usr/local/bin/ sudo cp redis-cli /usr/local/bin/
Next, we start the installation by going to utils folder,
cd .. cd utils
Then we start installation script by
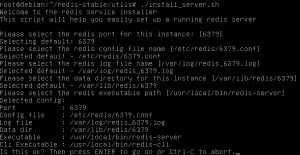
sudo ./install_server.sh
It should prompt you for different values. If you want to use the default values, just hit enter.
4. Testing Redis
Start redis command line by:
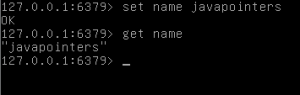
redis-cli
set name javapointers get name
Now you have successfully installed Redis Server!